The Canal du Midi water supply:
Riquet's ingenious system
Supplying water to a summit-level canal that is as long as the Canal du Midi requires a certain technique and expert knowledge in hydraulics. Thanks to his advanced studies and his many experiments, Pierre-Paul Riquet achieved what his predecessors had not managed to do and came up with ingenious solutions.
350 years after it was designed, the system created by Riquet still remains a masterpiece in hydraulic engineering!
The issue of the water supply was the main challenge in building the Canal du Midi
Costly earlier projects
To supply a summit-level canal such as the Canal du Midi, significant water resources are needed. These resources need to be at a higher altitude than the highest point of the waterway.
All the earlier projects for a canal ran into this tricky problem, and none of them found a solution. They all proposed to use the big rivers that flowed down from the Pyrenees (Garonne and Ariège) to provide water for the canal.
The various projects were abandoned because they were either technically impossible or extremely costly.
The ingenious solution designed by Riquet
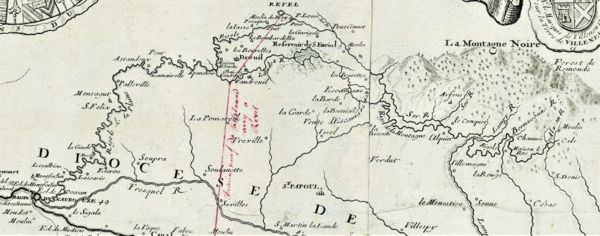
In the 1650s, Pierre-Paul Riquet looked into the advantage of using the smaller rivers of the Montagne Noire region, in the foothills of the Massif Central. Riquet planned on using the waters of the river Sor. He also planned on diverting the rivers from the Mediterranean basin to the Atlantic basin side, using a man-made channel in the Sor valley guiding to the Seuil de Naurouze, the watershed point where waters flow to the Atlantic on one side and the Mediterranean on the other.
Hydraulics experiments at Bonrepos
In the grounds of his residence, the Château de Bonrepos, near Toulouse, Riquet studied his hydraulics ideas. Using the various bodies of water on the estate, he carried out some small-scale experiments to see whether they would be feasible on a larger scale. The ingenuity of the solutions Riquet came up with, combined with the complexity of the supply system topography, made the Canal du Midi a masterpiece of hydraulic engineering.The plans for the Canal du Midi water supply system
The Montagne Noire and the waters of the Sor
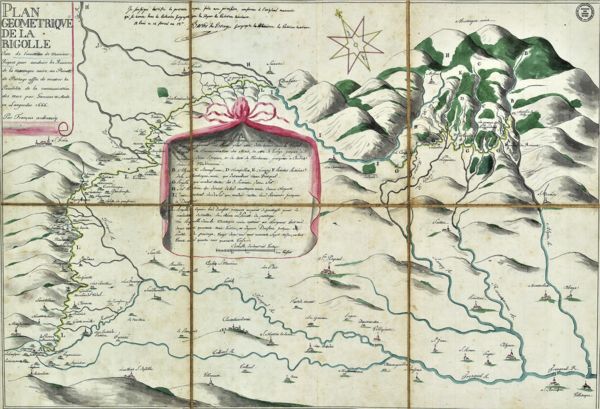
The project that Riquet presented to Colbert on 15 November 1662 was based on the creation of two sections of a man-made channel:
- The Rigole de la Montagne channel: at 500 metres above sea level, this channel diverts the waters of the Mediterranean basin in the Montagne Noire, from Alzeau to Conquet.
- The Rigole de la Plaine channel: after flowing across the watershed point between the Atlantic and Mediterranean basins, the water ends up in the Sor valley. It is then collected from the Sor, upstream from Revel, and channeled to the watershed point.
To make up for the scarce water resources in summer, Riquet planned on building a dozen small reservoirs. Riquet called them 'magasins d’eau' (water storehouses) or provision basins. In the end, these small basins were replaced by one single, vast reservoir on the Laudot river, a tributary of the Sor, at Saint-Ferréol.
A trial channel to win over Colbert
Colbert was interested in Riquet's project. He was aware that the construction of such a canal would turn France into an economic power, therefore gaining an advantage over Spain in particular. Louis XIV appointed a commission of experts to study the feasibility of the project.
Riquet was determined to win over the commission and show them that his project was completely viable, and so he offered to build a trial channel, at his own expense. In July 1665, his excavation teams began digging a small canal. In October, the waters from the Alzeau were flowing at Naurouze. Riquet's gamble paid off. There are still some remains of this trial channel which was built just above the channel that is now used to supply the canal.
Key elements of the water supply system in the Montagne Noire
The Rigole de Montagne channel
The Rigole de la Montagne, at an elevation of between 650 and 550 metres, collects the waters from the Mediterranean basin in the Montagne Noire region.
The Rigole de la Montagne originates from the streams on the south side of the mountain, and then flows into a waterway on the north side, the Sor, in the hamlet of Le Conquet, at 'Le Saut du Sor'. Once the Sor has been filled with the waters from this channel, the waters are deviated to the Rigole de la Plaine channel at the town of Sorèze, supplying water to the town of Revel and the Seuil de Naurouze.
In 1689, Vauban improved the canal and the water supply system. He connected the Rigole de la Montagne to Laudot stream via an underground route he called the Voûte Vauban in today's town of Cammazes.
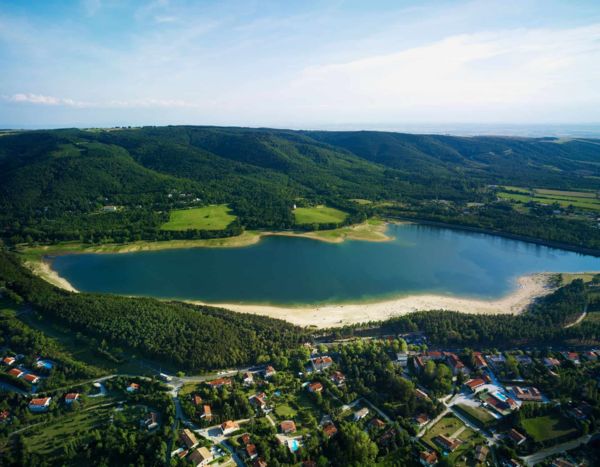
Saint-Ferréol Lake
Saint-Ferréol reservoir is at an elevation of 350 metres and has the capacity for 5,000,000 m3 of water!
This unique reservoir lake is used to supply water to the canal from toulouse to Carcassonne, and completes the supply of the entire canal in periods of drought.
It's also a delight for tourists and locals who enjoy this swimming and leisure area.
Saint-Ferréol reservoir
Saint-Ferréol reservoir lake gets its water supply from Laudot stream, and is then joined onto the Rigole de la Plaine channel, to supply water if needed at a place called 'Les Thoumazés'.
The Rigole de la Plaine channel
The Rigole de la Plaine (at an elevation of between 245 and 189 metres) is used to carry water to the Seuil de Naurouze, the highest point of the Canal du Midi.
The channel begins at Pont-Crouzet and then collects the waters of the Sor, then the Laudot and channels this water as far as Naurouze. The total length of the Rigole de la Plaine is 38.120 km, and it is approximately 2 metres wide.
At the Seuil de Naurouze, this watershed point, water flows west towards Toulouse, and east towards the Mediterranean.
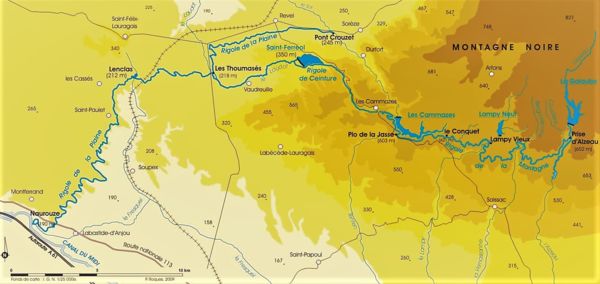
Water supply scheme of the Montagne Noire today
(1) Alzeau water inlet.
(2) Lampy: The engineer Garripuy created in 1782 the Lampy Neuf dam (reservoir with a capacity of 1.6 million m3 of water) upstream from the former Lampy Vieux dam, to increase the water reserves. This 2nd reservoir was created to supply the Canal de Jonction which connects the Canal du Midi to the Canal de la Robine, providing a second access to the sea.
(3) Le Conquet: Passage from the Mediterranean basin to the Atlantic basin. There is a sluice gate to control the flow from the Rigole de la Montagne, and excess water is directed towards the Sor.
(4) Cammazes Dam on the Sor, was built in 1956 by the 'Institution des Eaux de la Montagne Noire (IEMN)'. It has a storage capacity of 18,8 Mm3. It is supplied with water from the Sor and the channel at the Conquet weir. By decree, VNF holds the rights to the water of Cammazes Dam to supply the Canal du Midi. Its main purpose is to store water for domestic consumption and for crop irrigation.
(5) Les Cammazes: the Voute de Vauban or Cammazes tunnel was created by Vauban. It allows the Rigole de la Montagne channel to reach Laudot stream in another basin.
(6) Saint-Ferréol Lake supplied by the Laudot, which in turn is supplied by the waters of the Rigole de la Montagne channel.
(7) Pont Crouzet, in the foothills of the Montagne Noire, is where the water inlet for the Sor is located.
(8) Les Thoumasés: The Rigole de la Plaine channel and Laudot stream merge here. There is a spillway to evacuate excess water into the Laudot towards the Atlantic basin. The water needed to supply the Canal du Midi is directed to the Rigole de la Plaine channel towards the Mediterranean basin.
(9) Seuil de Naurouze: This is the highest point of the canal route. The Rigole de la Plaine flows into the Canal du Midi here.
The Canal du Midi supply system involved ingenious, never-before-seen construction work
Timeline of the construction work in the Montagne Noire region
Construction work in the Montagne Noire region began with the 'Montagne' and 'Plaine' channels. In April of the same year, the foundations began for Saint-Ferréol dam
Riquet sent boats to sail along the Rigole de la Plaine channel
The water supply system was operational and the first navigation trials between Naurouze and Toulouse were carried out. Saint-Ferréol dam was filled with water for the first time, but it wouldn't be finished until 1680.
Saint-Férréol dam was raised to increase its capacity. To fill the dam, the Rigole de la Montagne channel was extended by five kilometres from Conquet to Cammazes where it crosses over a ridge line via a tunnel and then rushes down from the Laudot source.
Another reservoir was added to the Montagne Noire water supply system at the Lampy river, to supply the Canal de Jonction and the Canal de la Robine.
This system was made all the more complex in 1950 when new reservoirs for the production of drinking water and farming irrigation were built. These reservoirs are connected to the hydraulics network of the Canal du Midi water supply system.
Over 350 years after its creation, Riquet's water supply system is now fully integrated into a vast network of water that now has a wide range of different uses!
Other water supply sources to support Riquet's system
The Montagne Noire network supplies water to the section of the Canal du Midi between Toulouse (Ponts-Jumeaux) and Carcassonne (Villedubert lock), covering a distance of 109 km (52 km for each basin and 5 km for the summit pound). The total capacity of the canal pounds is 3.65 Mm3.
It should be noted that the Montagne Noire channels are not the only water source for the canal. As I'm sure you're aware, this wouldn't be enough bearing in mind the water needed for the section that leads towards the Mediterranean (downstream from Carcassonne) for navigation and irrigation purposes.
Other water supply sources from Carcassonne to Béziers
There are four extra water inlets from rivers, to supply water to the canal from Carcassonne to Béziers (99 km) as well as for the Canal de Jonction (5 km). The capacity of the canal pounds is 3.3 Mm3, for this part of the Canal du Midi and 0.165 Mm3 for the Canal de Jonction.- Lachaux water inlet on the Fresquel in Villemoustoussou, now abandoned.
- Villedubert water inlet on the Aude, in Villedubert
- Orbiel water inlet on the river Orbiel in Trèbes, now abandoned.
- Cesse water inlet on the river Cesse in Mirepeisset
Three water inlets for the end of the Canal du Midi and the Canal de la Robine
These water inlets are the finals additions to the water supply system:
- The water inlet at Pont-Rouge dam in Béziers
On the left banks of the Orb, this water inlet provides any additional water needed from Béziers onwards. It is now virtually abandoned, except in exceptional cases. - Agde water inlet in the Hérault River
On the left banks of the Hérault, this water inlet provides water for the final section from Agde to Thau Lagoon. - Moussoulens water inlet
On the right banks of the Aude, this water inlet supplies the Canal de La Robine.